Phần 12 Install and config Sharding in MongoDB Replicaset
Phần 12 Install and config Sharding in MongoDB Replicaset
Phần 1: Lý thuyết
Introduction to MongoDB Sharding
The main purpose of using a NoSQL Database for most organizations is the ability to deal with the storage and compute demands of storing and querying high volumes of data. MongoDB Sharding can be seen as the way in which MongoDB deals with high volumes of data. It can be seen as the process in which large datasets are split into smaller datasets that are stored across multiple MongoDB Instances. This is done because querying on large datasets could lead to high CPU utilization on the MongoDB Server.
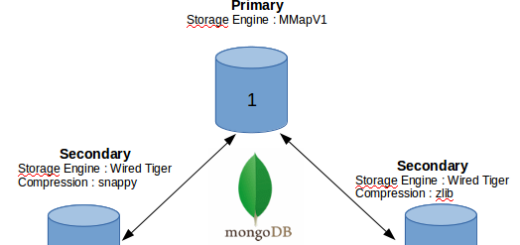
The following image shows the structure of a MongoDB Database:
Each MongoDB Database consists of a large number of Collections. Each Collection is made up of a large number of Documents that store data as Key-Value pairs. MongoDB Sharding breaks up a large Collection into smaller Collections called Shards. Splitting up large Collections into Shards allows MongoDB to execute queries without putting much load on the Server.
MongoDB Sharding can be implemented by creating a Cluster of MongoDB Instances. The following image shows how MongoDB Sharding works in a Cluster.
The three main components of Sharded Cluster are as follows:
1) Shard
Shard is the most basic unit of a Shared Cluster that is used to store a subset of the large dataset that has to be divided. Shards are designed in such a way that they are capable of providing high data availability and consistency.
2) Config Servers
Config Servers are supposed to store the metadata of the MongoDB Sharded Cluster. This metadata consists of information about what subset of data is stored in which Shard. This information can be used to direct user queries accordingly. Each Sharded Cluster is supposed to have exactly 3 Config Servers.
3) Query Routers
Query Routers can be seen as Mongo Instances that form an interface to the client applications. The Query Routers are responsible for forwarding user queries to the right Shard.
Benefits of MongoDB Sharding
MongoDB Sharding is important because of the following reasons:
In a setup in which MongoDB Sharding has not been implemented, the Master nodes handle the potentially large number of write operations whereas the Slave Nodes are responsible for read operations and maintaining backups. Since MongoDB Sharding utilizes Replica Sets, queries are distributed equally among all nodes.
The storage capacity of the Sharded Cluster can be increased without performing any complex hardware restructuring by simply adding additional Shards to the Cluster.
If one or more Shards in the Cluster go down, other Shards will continue to operate which means that the data stored in those active Shards can be accessed without any issues.
mongod --shardsvr --replSet rs0 --dbpath /var/lib/mongodb --bind_ip localhost,<hostname(s)|ip address(es)>
Để triển khai thì cần tạo replicaset cho cụm Data và Repicaset cho cụm cfg
#
Turning a Replica Set to a Sharded Cluster
Trong Shard Cluster, sẽ có 2 Role được add: mongos và mongod. Trong đó
mongos: config.mongos làm nhiệm vụ routing cho MongoDB cluster, nó xác định vị trí của các node mongo data trong cluster, và forward các truy vấn vào trong mongodata. Để hoạt động được mongos cần có mongod config, nơi mà chứa metadata của cluster. Tất cả mongos node phải chỉ định mongodb config hosts theo cùng 1 thứ tự, nếu config host đầu tiên bị lỗi mongos sẽ chuyển đến mongod tiếp theo ở trong list
mongos làm nhiệm vụ router kết nối các thành phần như mongo config và mongo data
mongod làm nhiệm vụ lưu trữ data
Phần 2: Thực hành tạo Shard Cluster.
Tóm tắt bài lab:
Bài lab làm theo mô hình dưới, Shard sẽ ko tạo replicaset, nếu muốn toạ replicaset cho shard thì cần tạo replicaset từ trước sau đó mới join shard.
Server mongo config cần phải join Replicaset. đây là server lưu trữ metadata.
Trong bài lab có hướng dẫn SSL authentication giữa các node, nhưng có thể bỏ qua ở bài lab này
https://www.linode.com/docs/guides/build-database-clusters-with-mongodb/
#############
2.1/ Trỏ file host vì không dùng DNS local.
10.0.2.11 mongo-config-1
10.0.2.12 mongo-config-2
10.0.2.13 mongo-config-3
10.0.2.14 mongo-query-router
10.0.2.15 mongo-shard-1
10.0.2.16 mongo-shard-2
2.2/ Tạo User admin trên node mongo-config-1
mongo
use admin
db.createUser({user: "mongo-admin", pwd: "Adminlab@@123", roles:[{role: "root", db: "admin"}]})
2.3/ Generate a Key file
bỏ qua bước này
openssl rand -base64 756 > mongo-keyfile
sudo mkdir /opt/mongo
sudo mv ~/mongo-keyfile /opt/mongo
sudo chmod 400 /opt/mongo/mongo-keyfile
sudo chown mongodb:mongodb /opt/mongo/mongo-keyfile
security:
keyFile: /opt/mongo/mongodb-keyfile
sudo systemctl restart mongod
2.4/ Cài đặt cho server config
Trên server mongo-config-1
nano /etc/mongod.conf
#
# mongod.conf
# for documentation of all options, see:
# http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/reference/configuration-options/
# Where and how to store data.
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongodb
journal:
enabled: true
# engine:
# mmapv1:
# wiredTiger:
# where to write logging data.
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
# network interfaces
net:
port: 27019
bindIp: 10.0.2.11
# how the process runs
processManagement:
timeZoneInfo: /usr/share/zoneinfo
#security:
#keyFile: /opt/mongo/mongo-keyfile
#operationProfiling:
#replication:
replication:
replSetName: configReplSet
#sharding:
sharding:
clusterRole: "configsvr"
## Enterprise-Only Options:
#auditLog:
#snmp:
Trên server mongo-config-2
# mongod.conf
# for documentation of all options, see:
# http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/reference/configuration-options/
# Where and how to store data.
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongodb
journal:
enabled: true
# engine:
# mmapv1:
# wiredTiger:
# where to write logging data.
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
# network interfaces
net:
port: 27019
bindIp: 10.0.2.12
# how the process runs
processManagement:
timeZoneInfo: /usr/share/zoneinfo
#security:
#operationProfiling:
#replication:
replication:
replSetName: configReplSet
#sharding:
sharding:
clusterRole: "configsvr"
## Enterprise-Only Options:
#auditLog:
#snmp:
Trên server mongo-config-3
# mongod.conf
# for documentation of all options, see:
# http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/reference/configuration-options/
# Where and how to store data.
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongodb
journal:
enabled: true
# engine:
# mmapv1:
# wiredTiger:
# where to write logging data.
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
# network interfaces
net:
port: 27019
bindIp: 10.0.2.13
# how the process runs
processManagement:
timeZoneInfo: /usr/share/zoneinfo
#security:
#operationProfiling:
#replication:
replication:
replSetName: configReplSet
#sharding:
sharding:
clusterRole: "configsvr"
## Enterprise-Only Options:
#auditLog:
#snmp:
Sau đó restart lại service mongod trên tất cả các node
sudo systemctl restart mongod
Kết nối vào server mongo config để cấu hình replicaset
mongo mongo-config-1:27019 -u mongo-admin -p --authenticationDatabase admin
rs.initiate( { _id: "configReplSet", configsvr: true, members: [ { _id: 0, host: "mongo-config-1:27019" }, { _id: 1, host: "mongo-config-2:27019" }, { _id: 2, host: "mongo-config-3:27019" } ] } )
# Kết quả
> rs.initiate( { _id: "configReplSet", configsvr: true, members: [ { _id: 0, host: "mongo-config-1:27019" }, { _id: 1, host: "mongo-config-2:27019" }, { _id: 2, host: "mongo-config-3:27019" } ] } )
{
"ok" : 1,
"$gleStats" : {
"lastOpTime" : Timestamp(1647336513, 1),
"electionId" : ObjectId("000000000000000000000000")
},
"lastCommittedOpTime" : Timestamp(0, 0)
}
configReplSet:SECONDARY> # sau khi cấu hình xong tự nhảy sang secondary nhưng kết nối lại là hết
Kiểm tra lại kết quả sau khi replicaset
rs.status()
#Kết quả
{
"set" : "configReplSet",
"date" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.726Z"),
"myState" : 2,
"term" : NumberLong(6),
"syncSourceHost" : "mongo-config-3:27019",
"syncSourceId" : 2,
"configsvr" : true,
"heartbeatIntervalMillis" : NumberLong(2000),
"majorityVoteCount" : 2,
"writeMajorityCount" : 2,
"votingMembersCount" : 3,
"writableVotingMembersCount" : 3,
"optimes" : {
"lastCommittedOpTime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1647405244, 2),
"t" : NumberLong(6)
},
"lastCommittedWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.211Z"),
"readConcernMajorityOpTime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1647405244, 2),
"t" : NumberLong(6)
},
"readConcernMajorityWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.211Z"),
"appliedOpTime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1647405244, 2),
"t" : NumberLong(6)
},
"durableOpTime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1647405244, 2),
"t" : NumberLong(6)
},
"lastAppliedWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.211Z"),
"lastDurableWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.211Z")
},
"lastStableRecoveryTimestamp" : Timestamp(1647405224, 2),
"members" : [
{
"_id" : 0,
"name" : "mongo-config-1:27019",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 2,
"stateStr" : "SECONDARY",
"uptime" : 66771,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1647405244, 2),
"t" : NumberLong(6)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04Z"),
"lastAppliedWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.211Z"),
"lastDurableWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.211Z"),
"syncSourceHost" : "mongo-config-3:27019",
"syncSourceId" : 2,
"infoMessage" : "",
"configVersion" : 1,
"configTerm" : 6,
"self" : true,
"lastHeartbeatMessage" : ""
},
{
"_id" : 1,
"name" : "mongo-config-2:27019",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 1,
"stateStr" : "PRIMARY",
"uptime" : 66768,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1647405244, 1),
"t" : NumberLong(6)
},
"optimeDurable" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1647405244, 1),
"t" : NumberLong(6)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04Z"),
"optimeDurableDate" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04Z"),
"lastAppliedWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.036Z"),
"lastDurableWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.036Z"),
"lastHeartbeat" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:04.113Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:03.998Z"),
"pingMs" : NumberLong(0),
"lastHeartbeatMessage" : "",
"syncSourceHost" : "",
"syncSourceId" : -1,
"infoMessage" : "",
"electionTime" : Timestamp(1647338472, 2),
"electionDate" : ISODate("2022-03-15T10:01:12Z"),
"configVersion" : 1,
"configTerm" : 6
},
{
"_id" : 2,
"name" : "mongo-config-3:27019",
"health" : 1,
"state" : 2,
"stateStr" : "SECONDARY",
"uptime" : 66768,
"optime" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1647405242, 1),
"t" : NumberLong(6)
},
"optimeDurable" : {
"ts" : Timestamp(1647405242, 1),
"t" : NumberLong(6)
},
"optimeDate" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:02Z"),
"optimeDurableDate" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:02Z"),
"lastAppliedWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:02.862Z"),
"lastDurableWallTime" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:02.862Z"),
"lastHeartbeat" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:03.239Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv" : ISODate("2022-03-16T04:34:03.048Z"),
"pingMs" : NumberLong(0),
"lastHeartbeatMessage" : "",
"syncSourceHost" : "mongo-config-2:27019",
"syncSourceId" : 1,
"infoMessage" : "",
"configVersion" : 1,
"configTerm" : 6
}
],
"ok" : 1,
"$gleStats" : {
"lastOpTime" : Timestamp(0, 0),
"electionId" : ObjectId("000000000000000000000000")
},
"lastCommittedOpTime" : Timestamp(1647405244, 2),
"$clusterTime" : {
"clusterTime" : Timestamp(1647405244, 2),
"signature" : {
"hash" : BinData(0,"AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA="),
"keyId" : NumberLong(0)
}
},
"operationTime" : Timestamp(1647405244, 2)
}
2.5/ Configure Query Router
Query Router được coi như cầu nối config server để đọc thông tin metadata để đọc ghi chính xác thông tin của các shard.
Tạo /etc/mongos.conf
#trong hướng dẫn của linode bị sai cấu trúc yaml
# where to write logging data.
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongos.log
# network interfaces
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 10.0.2.14
#security:
#keyFile: /opt/mongo/mongodb-keyfile
#sharding:
# configDB: "configReplSet/mongo-config-1:27019,mongo-config-2:27019,mongo-config-3:27019"
sharding:
configDB: "configReplSet/mongo-config-1:27019,mongo-config-2:27019,mongo-config-3:27019"
Sau đó chỉ cần start được service là sẽ sử dụng được thông tin login user mongo-admin/Adminlab@@123
Tạo service
/lib/systemd/system/mongos.service
#
[Unit]
Description=Mongo Cluster Router
After=network.target
[Service]
User=mongodb
Group=mongodb
ExecStart=/usr/bin/mongos --config /etc/mongos.conf
# file size
LimitFSIZE=infinity
# cpu time
LimitCPU=infinity
# virtual memory size
LimitAS=infinity
# open files
LimitNOFILE=64000
# processes/threads
LimitNPROC=64000
# total threads (user+kernel)
TasksMax=infinity
TasksAccounting=false
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
systemctl daemon-reload
#
sudo systemctl stop mongod
sudo systemctl enable mongos.service
sudo systemctl start mongos
2.6/ Add Shard to Cluster
Now that the query router is able to communicate with the config servers, we must enable sharding so that the query router knows which servers will host the distributed data and where any given piece of data is located.
bước tạo service cho mongos nhưng bị lỗi nên sẽ chạy thẳng theo như bên dưới
Do bị lỗi khi start service mongos
Unrecognized option: sharding.configDB
Tìm mãi không ra nên start theo command
sudo mongos -f /etc/mongos.conf
Login vào 2 server Shard cluster. ở đây không cấu hình Replicaset cho Shard Cluster
Trên server Shard 1
nano /etc/mongod.conf
#
# mongod.conf
# for documentation of all options, see:
# http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/reference/configuration-options/
# Where and how to store data.
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongodb
journal:
enabled: true
# engine:
# mmapv1:
# wiredTiger:
# where to write logging data.
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
# network interfaces
net:
port: 27017
# bindIp: 127.0.0.1
bindIp: 10.0.2.15
# how the process runs
processManagement:
timeZoneInfo: /usr/share/zoneinfo
#security:
#operationProfiling:
#replication:
#replication:
# replSetName: "replconfig01"
#sharding:
sharding:
clusterRole: shardsvr
## Enterprise-Only Options:
#auditLog:
#snmp:
Trong guide linode bị thiếu phần config sharding nên bị lỗi, do đó cần add thêm
Cấu hình tương tự cho server Shard 2
# mongod.conf
# for documentation of all options, see:
# http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/reference/configuration-options/
# Where and how to store data.
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongodb
journal:
enabled: true
# engine:
# mmapv1:
# wiredTiger:
# where to write logging data.
systemLog:
destination: file
logAppend: true
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
# network interfaces
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 10.0.2.16
# how the process runs
processManagement:
timeZoneInfo: /usr/share/zoneinfo
#security:
#operationProfiling:
#replication:
#sharding:
sharding:
clusterRole: shardsvr
## Enterprise-Only Options:
#auditLog:
#snmp:
Truy cập vào mongo shell trên mongo query router
mongo mongo-query-router:27017 -u mongo-admin -p --authenticationDatabase admin
Tiến hành add 2 Shard
sh.addShard( "mongo-shard-1:27017" )
sh.addShard( "mongo-shard-2:27017" )
#
mongos> sh.addShard( "mongo-shard-1:27017" )
#Ket qua
{
"shardAdded" : "shard0000",
"ok" : 1,
"operationTime" : Timestamp(1647399762, 1),
"$clusterTime" : {
"clusterTime" : Timestamp(1647399762, 1),
"signature" : {
"hash" : BinData(0,"AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA="),
"keyId" : NumberLong(0)
}
}
}
#
mongos> sh.addShard( "mongo-shard-2:27017" )
#Ket qua
{
"shardAdded" : "shard0001",
"ok" : 1,
"operationTime" : Timestamp(1647399947, 3),
"$clusterTime" : {
"clusterTime" : Timestamp(1647399947, 3),
"signature" : {
"hash" : BinData(0,"AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA="),
"keyId" : NumberLong(0)
}
}
}
Note
#Nếu cấu hình Replicaset cho Sharding
#Optionally, if you configured replica sets for each shard instead of single servers, you can add them at this stage with a similar command:
sh.addShard( "rs0/mongo-repl-1:27017,mongo-repl-2:27017,mongo-repl-3:27017" )
In this format, rs0 is the name of the replica set for the first shard, mongo-repl-1 is the name of the first host in the shard (using port 27017), and so on. You’ll need to run the above command separately for each individual replica set.
#Note
#Before adding replica sets as shards, you must first configure the replica sets themselves.
2.7/ Config Sharding
At this stage, the components of your cluster are all connected and communicating with one another. The final step is to enable sharding. Enabling sharding takes place in stages due to the organization of data in MongoDB. To understand how data will be distributed, let’s briefly review the main data structures:
Databases - The broadest data structure in MongoDB, used to hold groups of related data.
Collections - Analogous to tables in traditional relational database systems, collections are the data structures that comprise databases
Documents - The most basic unit of data storage in MongoDB. Documents use JSON format for storing data using key-value pairs that can be queried by applications
Kết nối vào mongo router
mongo mongo-query-router:27017 -u mongo-admin -p --authenticationDatabase admin
#create template DB
use exampleDB
#Enable Sharding
sh.enableSharding("exampleDB")
# To verify that the sharding was successful, first switch to the config database:
use config
#Next, run a find() method on your databases
db.databases.find()
#
{ "_id" : "exampleDB", "primary" : "shard0001", "partitioned" : true }
#
2.8/ Sharding Strategy
Có 2 loại
Range-based sharding
Hash-based sharding
2.9/ Enable Sharding at Collection Level
Now that the database is available for sharding and we’ve chosen a strategy, we need to enable sharding at the collections level. This allows the documents within a collection to be distributed among your shards. We’ll use a hash-based sharding strategy for simplicity.
Note
It’s not always necessary to shard every collection in a database. Depending on what data each collection contains, it may be more efficient to store certain collections in one location since database queries to a single shard are faster. Before sharding a collection, carefully analyze its anticipated contents and the ways it will be used by your application.
Connect to the mongo shell on your query router if you’re not already there:
mongo mongo-query-router:27017 -u mongo-admin -p --authenticationDatabase admin
use exampleDB
db.exampleCollection.ensureIndex( { _id : "hashed" } )
#Kết quả
{
"raw" : {
"mongo-shard-2:27017" : {
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : true,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
},
"ok" : 1,
"operationTime" : Timestamp(1647402763, 1),
"$clusterTime" : {
"clusterTime" : Timestamp(1647402763, 1),
"signature" : {
"hash" : BinData(0,"AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA="),
"keyId" : NumberLong(0)
}
}
}
shard the collection
mongos> sh.shardCollection( "exampleDB.exampleCollection", { "_id" : "hashed" } )
#Kết quả
{
"collectionsharded" : "exampleDB.exampleCollection",
"collectionUUID" : UUID("1ee63e75-4a92-482f-9926-7747cb97dd9a"),
"ok" : 1,
"operationTime" : Timestamp(1647402797, 8),
"$clusterTime" : {
"clusterTime" : Timestamp(1647402797, 8),
"signature" : {
"hash" : BinData(0,"AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA="),
"keyId" : NumberLong(0)
}
}
}
2.10/ Test cluster
Truy cập vào mongo shell
mongo mongo-query-router:27017 -u mongo-admin -p --authenticationDatabase admin
use exampleDB
for (var i = 1; i <= 500; i++) db.exampleCollection.insert( { x : i } )
# Kết quả
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
Check your data distribution:
mongos> db.exampleCollection.getShardDistribution()
#
Shard shard0001 at mongo-shard-2:27017
data : 8KiB docs : 253 chunks : 2
estimated data per chunk : 4KiB
estimated docs per chunk : 126
Shard shard0000 at mongo-shard-1:27017
data : 7KiB docs : 247 chunks : 2
estimated data per chunk : 3KiB
estimated docs per chunk : 123
Totals
data : 16KiB docs : 500 chunks : 4
Shard shard0001 contains 50.6% data, 50.6% docs in cluster, avg obj size on shard : 33B
Shard shard0000 contains 49.4% data, 49.4% docs in cluster, avg obj size on shard : 33B
=> Như vậy mỗi shard đã đều được phân phối các collections
2.11/ Kết nối với Shard Cluster qua Mongo Compass
https://www.linode.com/docs/guides/build-database-clusters-with-mongodb/
https://severalnines.com/database-blog/turning-mongodb-replica-set-sharded-cluster
https://vnsys.wordpress.com/2021/05/24/deploy-mongodb-sharded-cluster/
https://hevodata.com/learn/implementing-mongodb-sharding-6-easy-steps/